Introduction of Altered Antigens to Produce an Immune Response
Existing therapies for AIH are based on non. Abnormal reaction to an antigen.
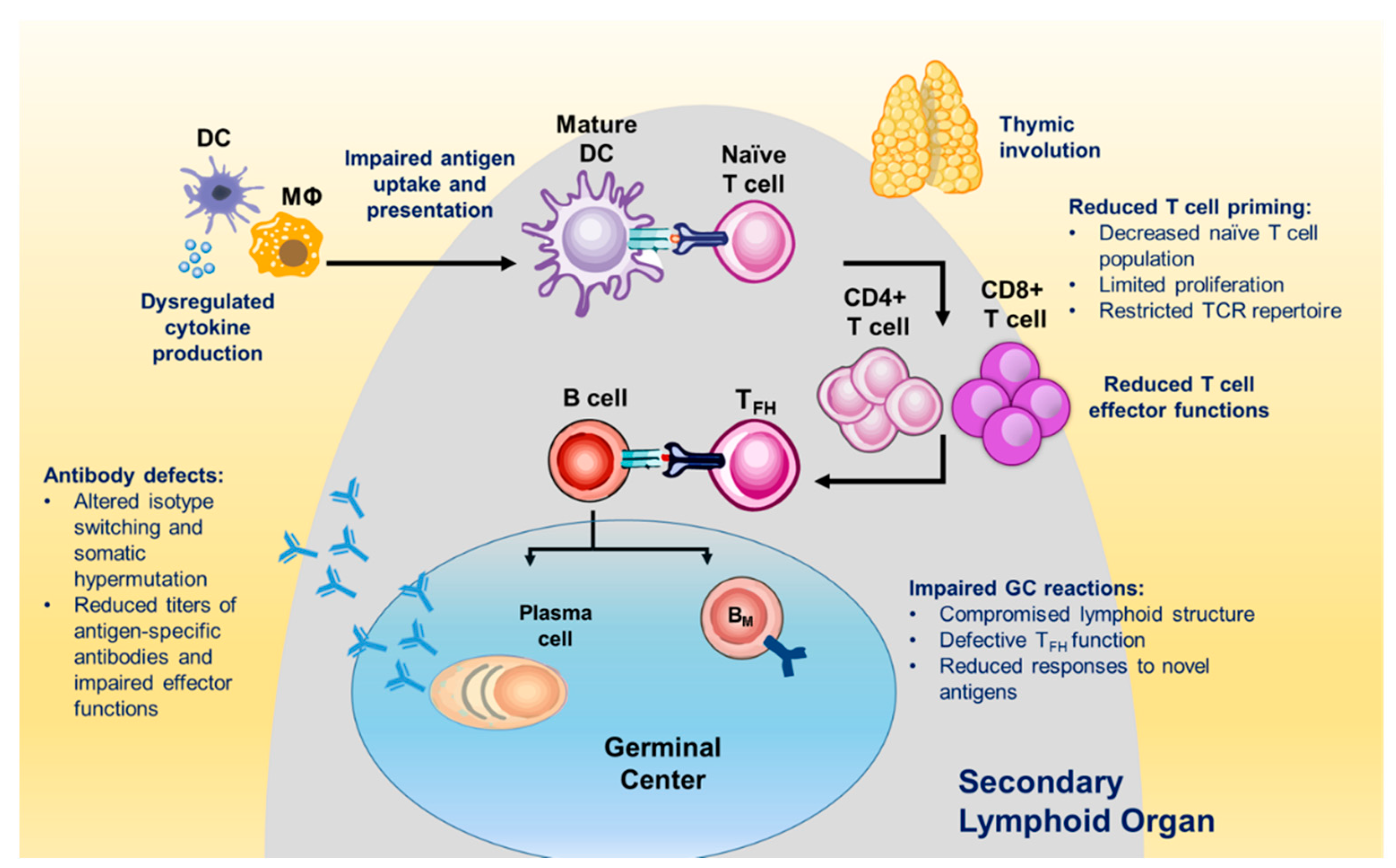
Vaccines Free Full Text B And T Cell Immunity In Tissues And Across The Ages Html
Cytokines are a large diverse family of small proteins or glycoproteins usually smaller than 30 kDa.

. In the liver after binding to target cells such as APCs EVsexosomes carrying peptide-MHC class II complexes are taken up by endocytosis and can induce three different immune responses. T lymphocytes attack antigens directly and help control the immune response. Although initially described for their.
In the case of autoimmune diseases self-antigens are presented to T cells which then initiates an immune response against our own tissues. Both the innate and adaptive levels of the immune response involve secreted proteins receptor-mediated. B lymphocytes become cells that produce antibodies.
Unlike the germ-line-encoded recognition molecules of the innate immune response the antigen-specific receptors of the adaptive response are encoded by genes that are assembled by somatic rearrangement of germ-line gene elements to form intact T cell receptor TCR and immunoglobulin B cell antigen receptor. The antigens have a molecular mass of 14000 to 600000 Da. Fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system.
In order to mount and coordinate an effective immune response a mechanism by which lymphocytes inflammatory cells and haematopoietic cells can communicate with each other is required. Immune responses in some mucosal tissues such as the Peyers patches see Chapter 211 Figure 21110 in the small intestine take up particulate antigens by specialized cells known as microfold or M cells Figure 2152. Mucosal tissues are major barriers to the entry of pathogens into the body.
Memory T and B cells are produced during an adaptive immune response allowing for a faster and more effective response to reinfection. The antigen should be a foreign substance to induce an immune response. The IgA and sometimes IgM antibodies in mucus and other secretions can bind to the pathogen and in the cases of many viruses and bacteria neutralize them.
Usually to be activated T cells require the help of another immune cell which breaks antigens into fragments called antigen processing Recognition and then presents antigen from the infected or abnormal cell to the T cell. The adaptive immune response to these antigens is so versatile that it can respond to nearly any pathogen. It is not induced by infection or vaccination but works to reduce the workload for the adaptive immune response.
This deterioration of the immune response is characterized by genetic epigenetic alterations in immune cells that are driven by chronic or repeated exposure to antigens derived from. These cells allow the body to sample potential pathogens from the intestinal lumen. Cytokines perform this function.
They are mainly proteins and polysaccharides. Substance that when entering the body prompts the generation of antibodies causing an immune response. Neutralization is the process of coating a pathogen with antibodies making it.
The antigen must encounter the B-lymphocytes T-lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells APCs capable of carrying out an adaptive immune response. Immune responses induced with these sources of altered antigen reacted with various processed forms of native syngeneic protein and could induce both tumor rejection and autoimmunity. Naive B-lymphocytes T4-lymphocytes and T8-lymphocytes must recognize epitopes of an antigen by means of antigen-specific receptor molecules on their surface and become activated.
The immune surveillance of transformedtumour cells drives alteration of the antigen processing and presentation pathways to evade detection and hence. 1 the peptide-MHC class II complex is directly presented by the APC to CD4 T cell eliciting T cell priming in an immunological synapse that involves co-stimulatory molecules. We thus consider that the immune system gathers information by binding to parasite antigens with a failure to obtain that information a failure to recognize and bind to a parasite antigen posing a serious risk to the organisms health and we also note that avoiding being observed by immune systems is a legitimate and not uncommon strategy.
The properties of antigens are as follows. Chapter 9 test yourself. This increase in specificity comes because the adaptive immune response has a unique way to develop as many as 10 11 or 100 trillion different receptors to recognize nearly every conceivable pathogen.
They also release chemicals known as cytokines which control the entire immune response. The precise etiology of AIH remains unknown. An antigen-presenting cell APC is an immune cell that detects engulfs and informs the adaptive immune response about an infection.
Innate immunity occurs naturally because of genetic factors or physiology. Most antigens defined on human cancers are expressed both by malignant and normal cells 1 4. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH.
The T cell then multiplies and specializes into different types of T cells. The innate immune system contains cells that detect potentially harmful antigens and then inform the adaptive immune response about the presence of these antigens. How could so many different types of antibodies be encoded.
Once detected T cells become activated and either directly kill the infected transformed cells CD 8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes or orchestrate the activation of the adaptive immune response CD 4 T cells. When a pathogen is detected these APCs will phagocytose the. Foreign or non-self protein that triggers the immune response antigen-presenting cell APC immune cell that detects engulfs and informs the adaptive immune response about an infection by presenting the processed antigen on the cell surface autoimmune response inappropriate immune response to host cells or self-antigens cell-mediated immune response adaptive.
Med term chapter 6. Along with genetic epigenetic and environmental factors pathogenic mechanisms such as molecular mimicry altered antigen presentation and dysregulated immune responses against liver autoantigens can lead to immune tolerance breakdown 3 1022 Figure 1. An antigen-presenting cell APC is an immune cell that detects engulfs and informs the adaptive immune response about an infection.
The immune system comprises both innate and adaptive immune responses. The Mucosal Immune Response. Introduction of altered antigens to produce an immune response.
Antigen receptors are genetically altered clonal receptors that bind to antigens presented on antigen-presenting cells by Major Histocompatibility Complex MHC molecules. Introduction of altered antigens viruses or bacteria into the body to produce an immune response and protect against disease. When a pathogen is detected these APCs will phagocytose the.
Dendritic cells then take the. The more chemically complex they are the more immunogenic they will be. I persistent or recurrent pathogens eg.
T-cell responses are induced by antigen presenting cells APC and signals from the microenvironment. Antibodies attach to a specific antigen and make it easier for the immune cells to destroy the antigen. Antigen persistence and inflammatory microenvironments in chronic infections and cancer can induce a tolerant state in T-cells resulting in hyporesponsiveness loss of effector function and weak biochemical signaling patterns in response to antigen.
For example in Graves disease TSHR thyroid stimulating hormone receptor acts as a self-antigen and is presented to T. The innate immune system contains cells that detect potentially harmful antigens and then inform the adaptive immune response about the presence of these antigens. It is important to note that APCs may deliver foreign antigens or self-antigens.
Organ in the mediastinum that produces T-cell lymphocytes and aids in the immune response.
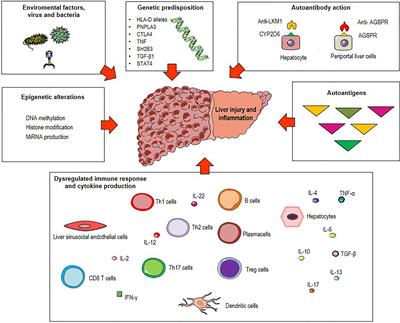
Frontiers Impact Of Antigen Presentation Mechanisms On Immune Response In Autoimmune Hepatitis Immunology

Dysregulation Of Humoral Immunity In Chronic Infection Cooper 2020 Immunology Amp Cell Biology Wiley Online Library

An Introduction To Antibodies Antigens Epitopes And Antibodies
0 Response to "Introduction of Altered Antigens to Produce an Immune Response"
Post a Comment